Changing the main MySQL version on the server with ISPmanager5
Instructions to change the basic version of MySQL on the server with the ISPmanager control panel
By default, the MySQL server on Ubuntu 18.04 will be installed version 5.7.
mysqladmin Ver 8.42 Distrib 5.7.25, for Linux on x86_64
Copyright (c) 2000, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Server version 5.7.25-0ubuntu0.18.04.1
Protocol version 10
Connection Localhost via UNIX socket
UNIX socket /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock
Uptime: 44 min 19 sec
Threads: 1 Questions: 50 Slow queries: 0 Opens: 115 Flushing tables: 1 Open tables: 24 Queries per second avg: 0.018
We strongly recommend backing up or snapshot all your order data before working on the server
If you need to upgrade to MySQL version 8.0, do the following steps: Remove MySQL server from ISPmanager section Abilities. With this action we remove ispmanager-pkg-mysql package and also remove MySQL server in Database Servers section

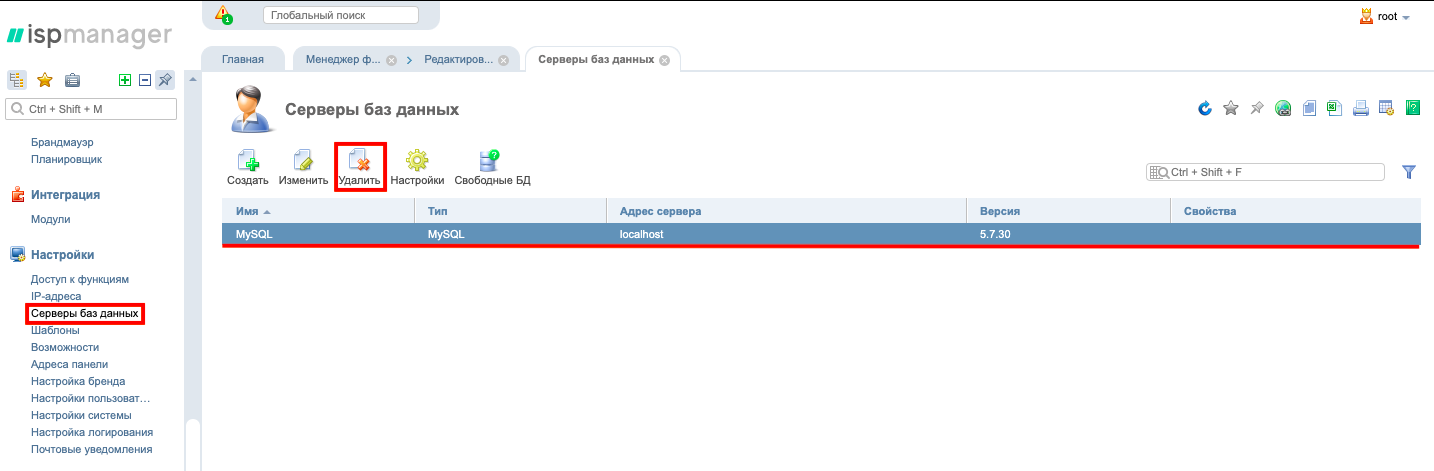
The beginning of the installation
Connect to the server via SSH and enter the command that updates the lists of packages from the repositories to get information about the latest versions of packages and their dependencies.
sudo apt update
Enter a command that retrieves new versions of packages that exist on the server:
sudo apt upgrade
Download the file using wget:
wget -c https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql-apt-config_0.8.15-1_all.deb
root@kvmde54-19861:~# wget -c https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql-apt-config_0.8.15-1_all.deb
--2020-06-01 14:03:09-- https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql-apt-config_0.8.15-1_all.deb
Resolving dev.mysql.com (dev.mysql.com)... 137.254.60.11
Connecting to dev.mysql.com (dev.mysql.com)|137.254.60.11|:443... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 302 Found
Location: https://repo.mysql.com//mysql-apt-config_0.8.15-1_all.deb [following]
--2020-06-01 14:03:10-- https://repo.mysql.com//mysql-apt-config_0.8.15-1_all.deb
Resolving repo.mysql.com (repo.mysql.com)... 23.44.197.55
Connecting to repo.mysql.com (repo.mysql.com)|23.44.197.55|:443... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 35532 (35K) [application/x-debian-package]
Saving to: 'mysql-apt-config_0.8.15-1_all.deb'
mysql-apt-config_0.8.15-1_ 100%[========================================>] 34.70K --.-KB/s in 0.008s
2020-06-01 14:03:10 (4.40 MB/s) - 'mysql-apt-config_0.8.15-1_all.deb' saved [35532/35532]
To check that the file downloaded, type:
ls
root@kvmde54-19861:~# ls
mysql-apt-config_0.8.15-1_all.deb ubuntu-echo
Next, unpack and install it:
sudo dpkg -i mysql-apt-config
Next, a window will appear in which you should check that it is MySQL Server & Cluster (Currently selected: mysql-8.0)
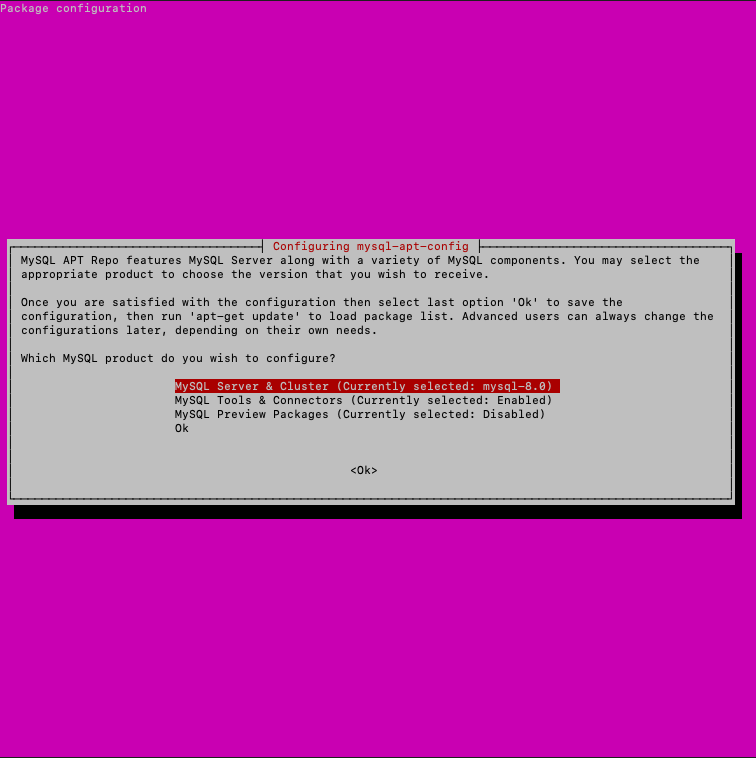
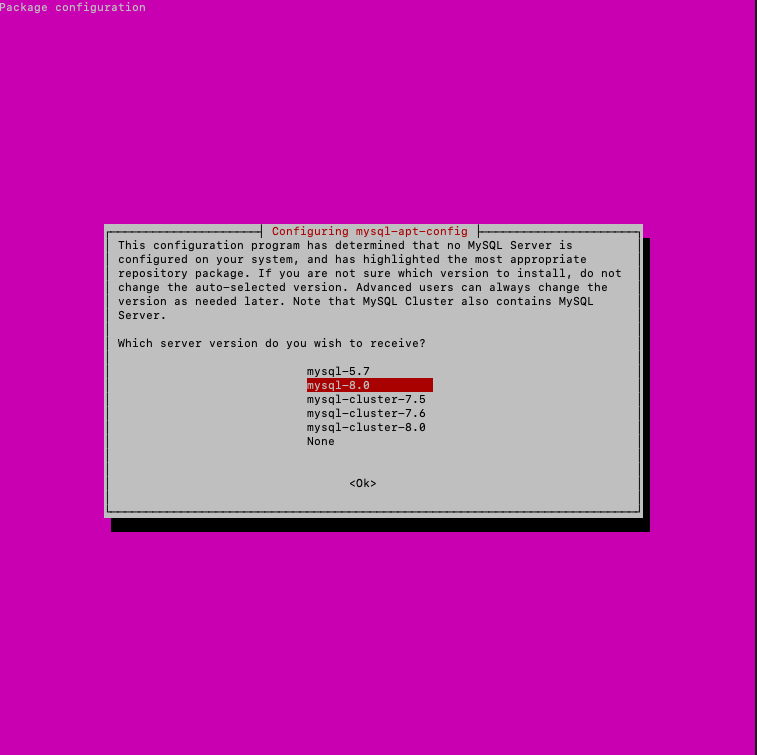
Next, enter the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
Install MySQL server:
sudo apt install mysql-server
A window will open in which you need to enter a new root password for MySQL (Ubuntu and MySQL passwords may be different)
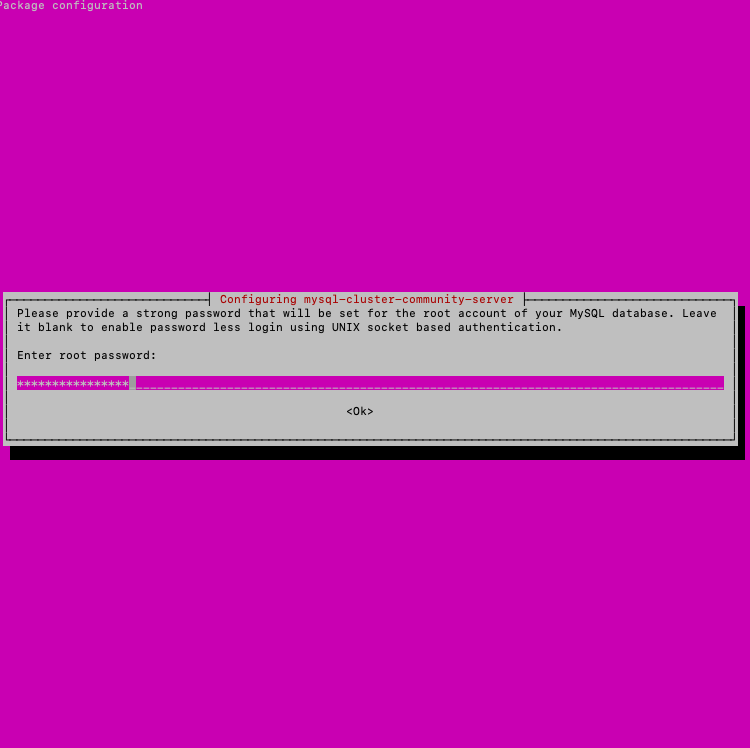
Next, let's click Ok
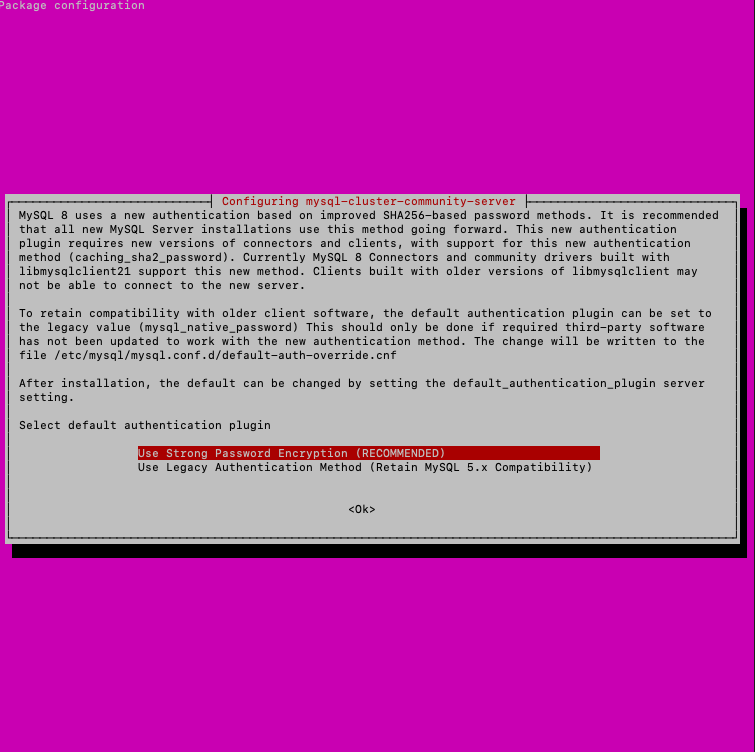
In the window, where it says about new MySQL 8 Authentication - click Use Strong Password Encryption (Recommended)
Next, we enter the command:
mysql_secure_installation
Enter the MySQL password.
Further security questions can be answered as follows
root@kvmde54-19861:~# mysql_secure_installation
Securing the MySQL server deployment.
Connecting to MySQL using a blank password.
VALIDATE PASSWORD COMPONENT can be used to test passwords
and improve security. It checks the strength of password
and allows the users to set only those passwords which are
secure enough. Would you like to setup VALIDATE PASSWORD component?
Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No: N
Please set the password for root here.
New password
Re-enter new password
By default, a MySQL installation has anonymous user,
allowing anyone to log into MySQL without having to have
a user account created for them. This is intended only for
testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother.
You should remove them before moving into a production
environment.
Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Success.
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from
'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at
the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Success.
By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that
anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing,
and should be removed before moving into a production
environment.
Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
- Dropping test database...
Success.
- Removing privileges on test database...
Success.
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes
made so far will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Success.
All done!
To check that MySQL is working, type:
systemctl status mysql
root@kvmde54-19861:~# systemctl status mysql
Mysql.service - MySQL Community Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mysql.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Drop-In: /etc/systemd/system/mysql.service.d
└─nofile.conf
Active: active (running) since Mon 2020-06-01 14:15:34 CEST; 1min 49s ago
Docs: man:mysqld(8)
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/en/using-systemd.html
Main PID: 31770 (mysqld)
Status: "Server is operational"
Tasks: 39 (limit: 1108)
CGroup: /system.slice/mysql.service
└─31770 /usr/sbin/mysqld
Jun 01 14:15:33 kvmde54-19861.fornex.org systemd[1]: Starting MySQL Community Server...
Jun 01 14:15:34 kvmde54-19861.fornex.org systemd[1]: Started MySQL Community Server.
Enter a command to check that MySQL 8.0 is installed, not MySQL5.*:
mysqladmin -u root -p version
root@kvmde54-19861:~# mysqladmin -u root -p version
Enter password
mysqladmin Ver 8.0.20 for Linux on x86_64 (MySQL Community Server - GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Server version 8.0.20
Protocol version 10
Connection Localhost via UNIX socket
UNIX socket /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock
Uptime: 2 min 1 sec
Threads: 2 Questions: 11 Slow queries: 0 Opens: 128 Flushing tables: 3 Open tables: 49 Queries per second avg: 0.090
MySQL version upgraded to version 8.0.20
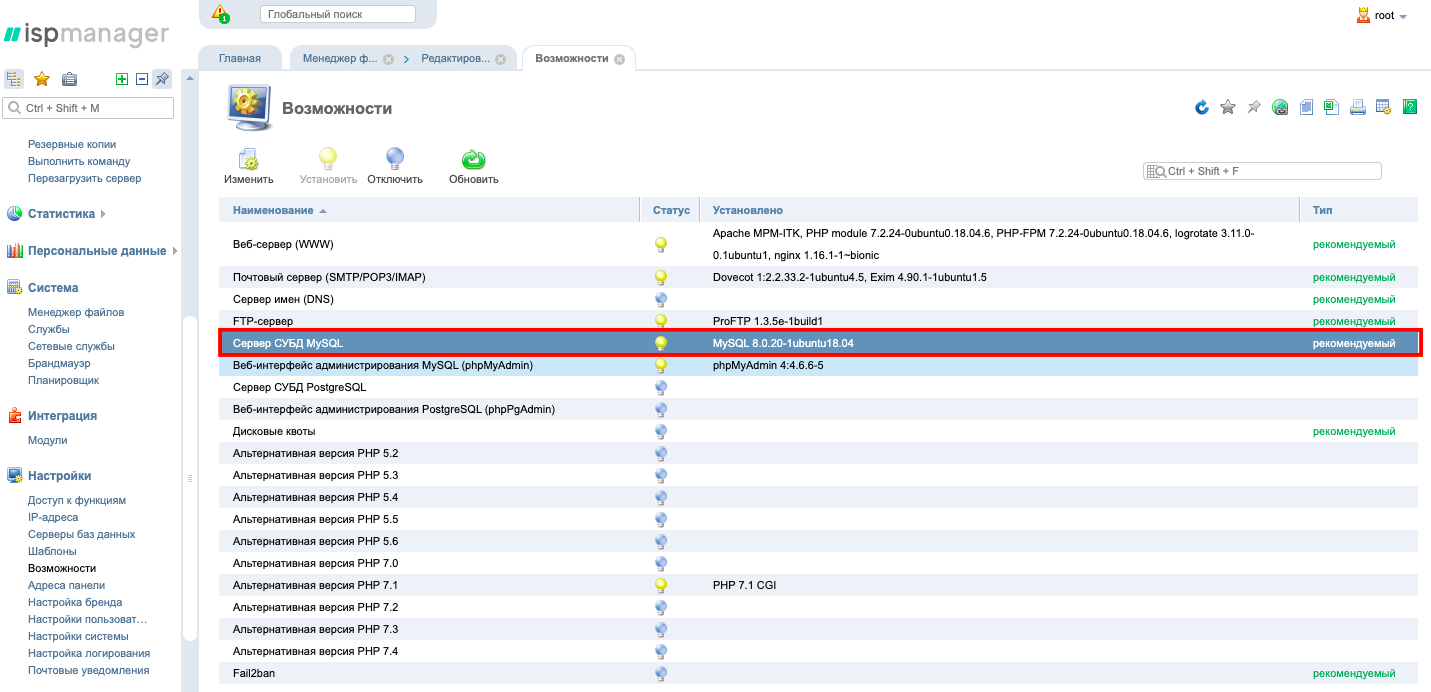
Now in the control panel, under Abilities let's install MySQL-server.

After the installation is complete, we will see that MySQL version is changed to 8.0.20.
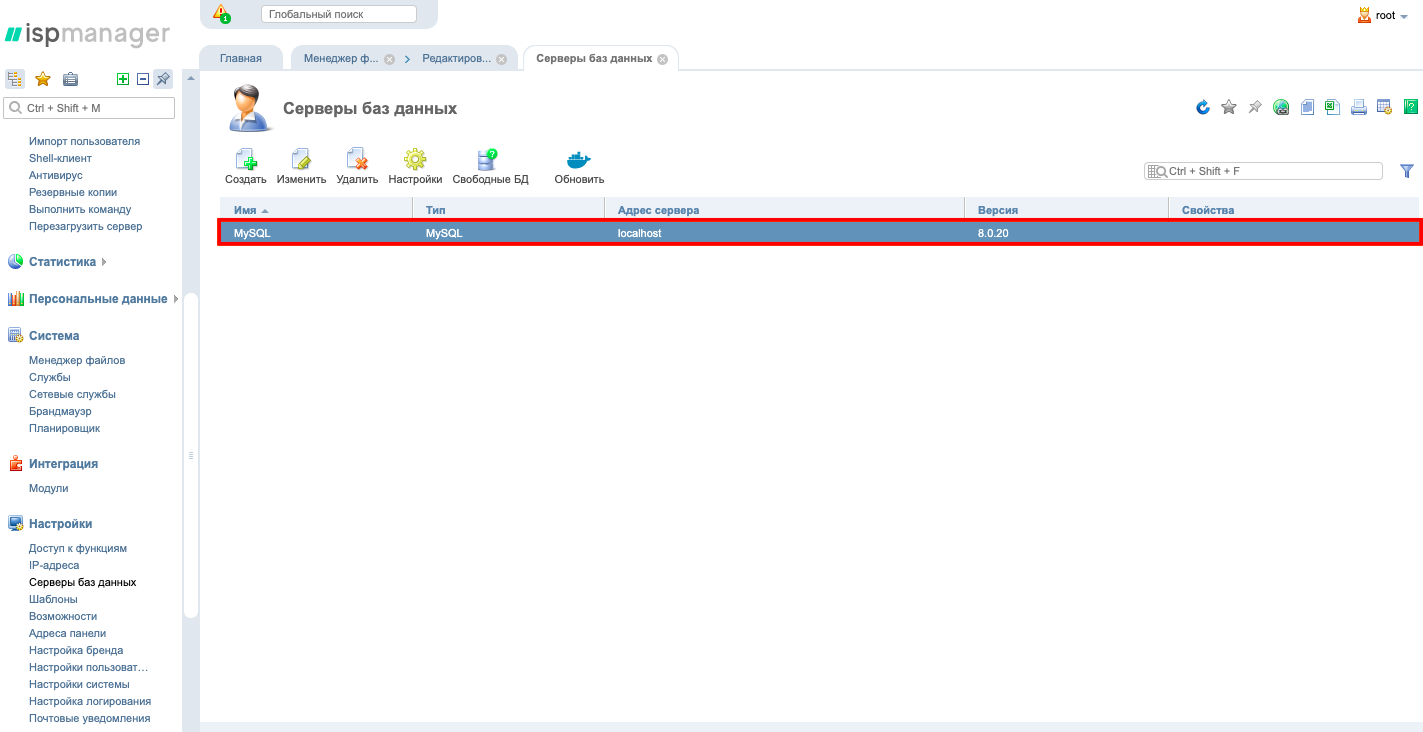
There will also be a server in the DB Servers section.
If you have already tried to install MySQL and had an error at some point, run these commands to start the process again:
sudo -i
service mysql stop
killall -KILL mysql mysqld_safe mysqld
apt-get --yes purge mysql-server mysql-client
apt-get --yes autoremove --purge
apt-get autoclean
deluser --remove-home mysql
delgroup mysql
rm -rf /etc/apparmor.d/abstractions/mysql /etc/apparmor.d/cache/usr.sbin.mysqld /etc/mysql /var/lib/mysql /var/log/mysql* /var/log/upstart/mysql.log* /var/run/mysqld
updatedb
exit
If you have configuration difficulties or have additional questions, you can always contact our support team via Ticket system.